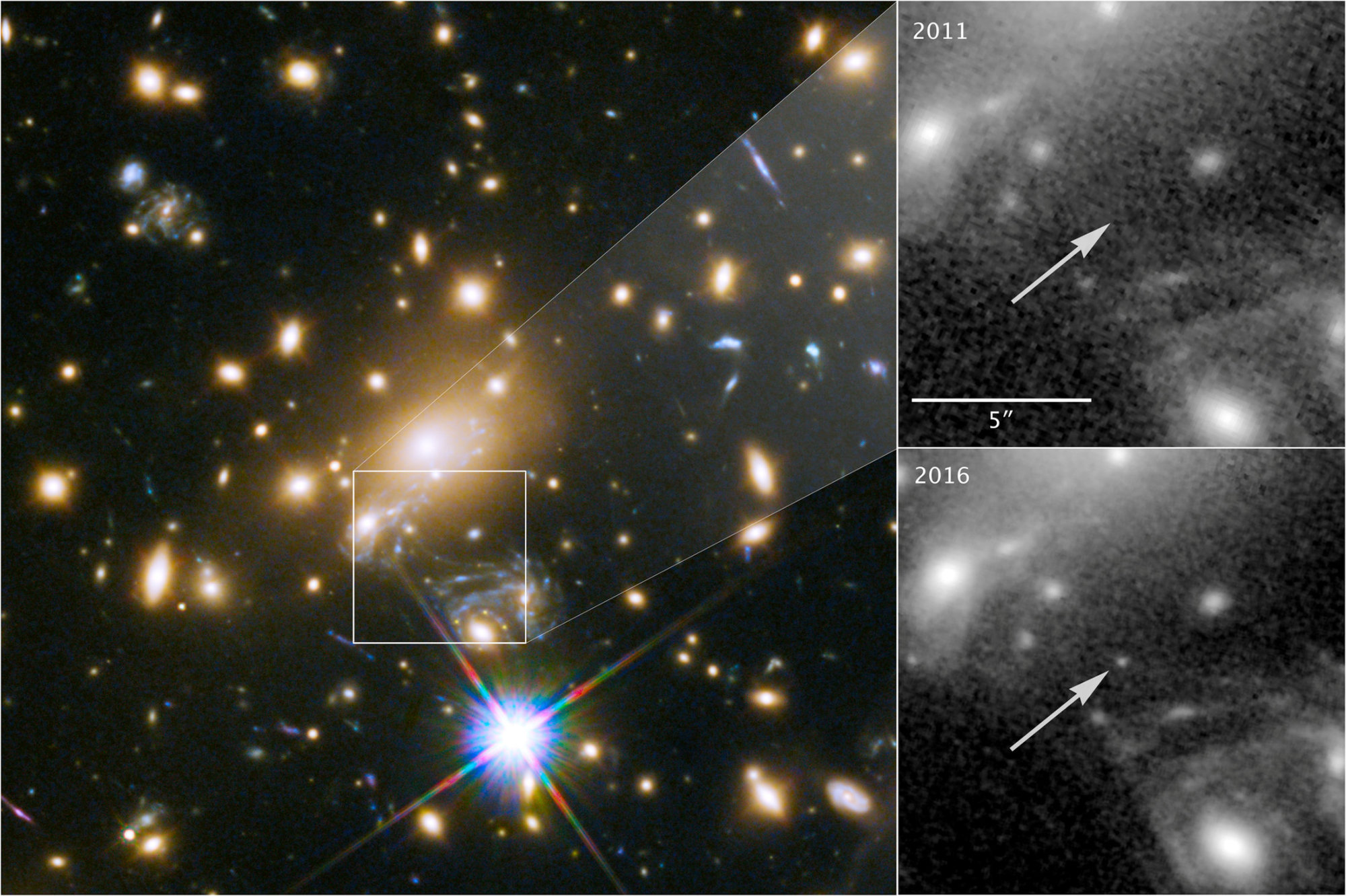
Scientists have detected the most distant star ever viewed, a blue behemoth located more than halfway across the universe and named after the ancient Greek mythological figure Icarus.
Researchers said on Monday they used NASA's Hubble Space Telescope to spot the star, which is up to a million times more luminous and about twice as hot as our sun, residing 9.3 billion lights years away from Earth. It is a type of star called a blue supergiant.
The star, located in a distant spiral galaxy, is at least 100 times farther away than any other star previously observed, with the exception of things like the huge supernova explosions that mark the death of certain stars. Older galaxies have been spotted but their individual stars were indiscernible.


















With your current subscription plan you can comment on stories. However, before writing your first comment, please create a display name in the Profile section of your subscriber account page.