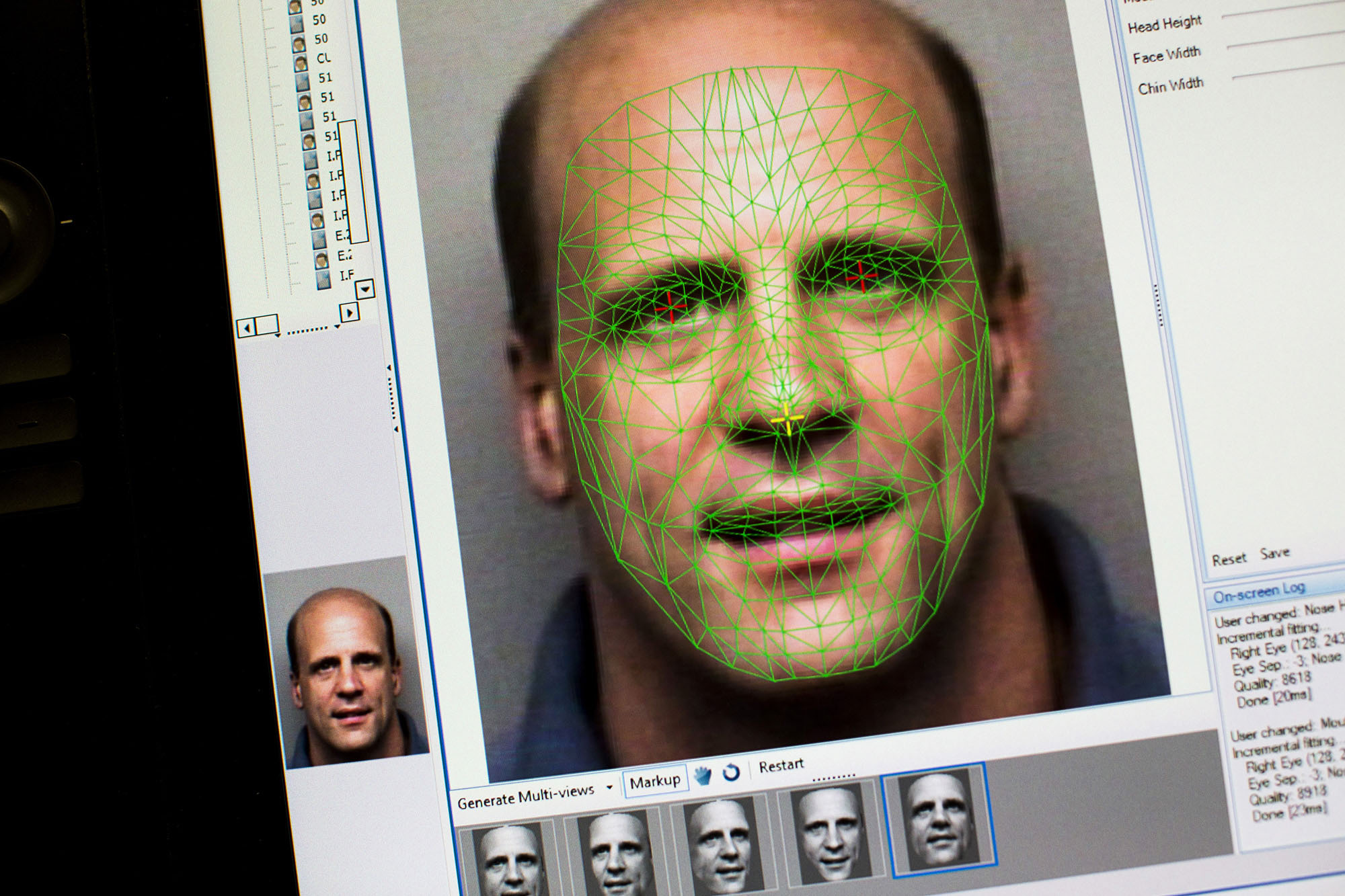
The faces of more than 120 million people are in searchable photo databases that state officials assembled to prevent driver's license fraud but that increasingly are used by police to identify suspects, accomplices and even innocent bystanders in a wide range of criminal investigations.
The facial databases have grown rapidly in recent years and generally operate with few legal safeguards beyond the requirement that searches are conducted for "law enforcement purposes." Amid rising concern about the National Security Agency's high-tech surveillance aimed at foreigners, it is these state-level facial-recognition programs that more typically involve American citizens.
The most widely used systems were honed on the battlefields of Afghanistan and Iraq as soldiers sought to identify insurgents. The increasingly widespread deployment of the technology in the United States has helped police find murderers, bank robbers and drug dealers, many of whom leave behind images on surveillance videos or social-media sites that can be compared against official photo databases.

















With your current subscription plan you can comment on stories. However, before writing your first comment, please create a display name in the Profile section of your subscriber account page.